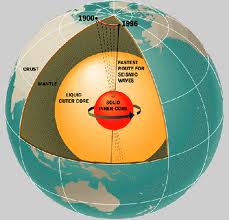
Professor Richard Holme, from the School of Environmental Sciences, studied the variations and fluctuations in the length of day over a one to 10 year period between 1962 and 2012. The study took account of the effects on the Earth’s rotation of atmospheric and oceanic processes to produce a model of the variations in the length of day on time scales longer than a year. Professor Holme said: “The model shows well-known variations on decadal time scales, but importantly resolves changes over periods between one and 10 years. Previously these changes were poorly characterized; the study shows they can be explained by just two key signals, a steady 5.9 year oscillation and episodic jumps which occur at the same time as abrupt changes in the Earth’s magnetic field, generated in the Earth’s core.” He added: “This study changes fundamentally our understanding of short-period dynamics of the Earth’s fluid core. It leads us to conclude that the Earth’s lower mantle, which sits above the Earth’s outer core, is a poor conductor of electricity giving us new insight into the chemistry and mineralogy of the Earth’s deep interior.” –Space Daily
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
