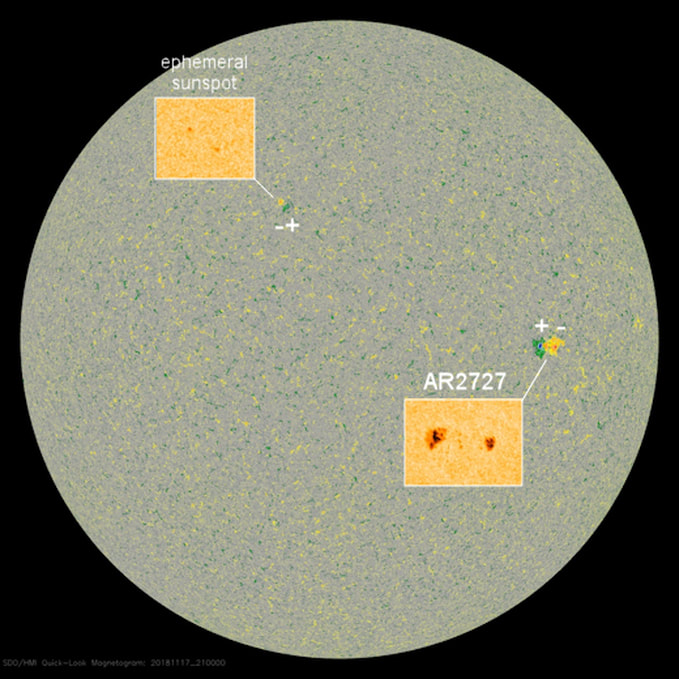
Note sunspot AR2727 just north of the sun's equator. It is a member of decaying Solar Cycle 24, the cycle that peaked back in 2012-2014. Next, compare its magnetic polarity to that of the other, unnumbered sunspot high above it. They are opposite. According to Hale's Law, this means the two sunspots belong to different solar cycles. The high latitude sunspot appears to be a harbinger of Solar Cycle 25.
Solar cycles always mix together at their boundaries. Indeed, ephemeral sunspots possibly belonging to Solar Cycle 25 have already been reported on Dec. 20, 2016, and April 8, 2018. Now we can add Nov. 17, 2018, to list. The slow transition between Solar Cycle 24 and Solar Cycle 25 appears to be underway.
What does this mean? First, it suggests that the solar cycle is still operative. This contradicts widespread internet buzz that a Grand Minimum is in the offing, with no new sunspots expected for decades as the solar cycle grinds to a halt. Second, if patterns of previous solar cycles hold, Solar Minimum is not finished. It will probably continue to deepen in the year or so ahead even as new Solar Cycle 25 sunspots occasionally pop up, promising an ultimate end to the lassitude.
www.spaceweather.com
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed