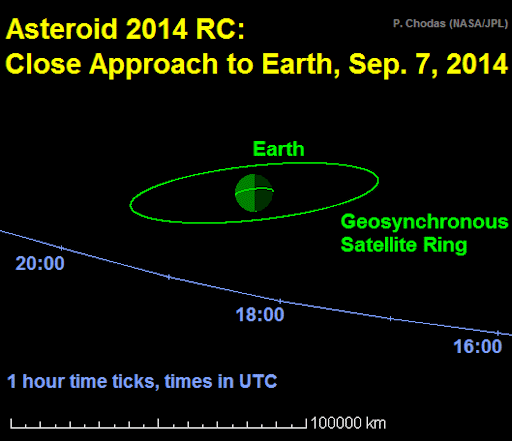
Asteroid 2014 RC was discovered on the night of August 31 by the Catalina Sky Survey near Tucson, Arizona, and independently detected the next night by the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope, located on the summit of Haleakalā on Maui, Hawaii. Follow-up observations quickly confirmed the orbit of 2014 RC: it comes from just beyond the orbit of Mars.
The close appproach of this space rock offers researchers an opportunity for point-blank studies of a near-Earth asteroid. Even amateur astronomers will be able to track it. Around the time of closest approach, it will brighten to magnitude +11.5 as it zips through the constellation Pisces. This means it will be invisible to the naked eye but a relatively easy target for backyard telescopes equipped with CCD cameras. [ephemeris] [3D orbit]
According to NASA, "[the orbit of 2014 RC] will bring it back to our planet's neighborhood in the future. The asteroid's future motion will be closely monitored, but no future threatening Earth encounters have been identified."
www.spaceweather.com
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed